How To Repair Old Plaster Walls + "Comment"
Repairing of plaster walls is needed from time to fourth dimension as the edifice ages. The near mutual problem with plaster walls is crumbling, water harm, cracking or pulling abroad from the lath backside information technology. Repairing procedure of plaster walls is presented in the following sections.
Repairing of Plaster walls
Procedures involved in repair of plaster are:
1. Identify Plaster Wall Problem
The type of damage shall exist specified prior to the commence of repairing operation. In this way, the most suitable technique and equipment can be employed to repair the damage and best effect could be accomplished.
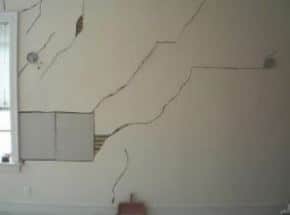
Table 1 provide types of plaster wall problems and their causes, and Fig.1 to Fig.3 shows number of plaster wall problems that need to exist repaired.
Tabular array i Common types of plaster wall trouble and their causes
| Common types of plaster wall problem | Cause of the plaster wall problem |
| Cracks | Hairline cracks due to moisture evaporation, delaminating crack because plaster pulling abroad from the lath behind it, and Settlement Cracks because of building settlement. |
| Impairment | activity inside the home like a standoff due to moving a piece of article of furniture |
| Blistering | improper slaking of lime particles in the plaster |
| Flaking | poor bond |
| Discoloration | Water seepage |


2. Setting up Scaffolding
Scaffolding is required for the proper execution of the repair work should be erected. Ladder tin also be used in case of scaffolding if the piece of work can exist done safely.
3. Protective Measure
Doors, windows, floors, articles of article of furniture etc. and such other parts of the building should be protected from being splashed by mortar.
4. Cutting of Quondam Plaster
The mortar of the patch, where the existing plaster has cracked, crumbled or sounds hollow when gently tapped on the surface, is offset removed.
The patch is be cut out to a square or rectangular shape at position where repairing is needed. The edges of cut plaster is made under cut to provide a peachy joint.
5. Training of Surface
The masonry joints which go exposed after removal of old plaster is raked out to a minimum depth of x mm in the case of brick work and 20 mm in the instance of stone piece of work.
The raking is carried out uniformly with a raking tool, and loose mortar is dusted off. The surface is then thoroughly washed with water, and kept wet till plastering is commenced.
In case of concrete surfaces, the quondam plaster is thoroughly scrubbed with wire brushes later on the plaster had been cut out, and pock marked the surface is roughened by wire brushing, and all the resulting dust and loose particles cleaned off. The surface is washed and cleaned and kept wet till plastering is commenced.

six. Awarding of Plaster
Mortar of specific mix such every bit ane:4 or 1:half dozen with the practiced quality plaster sand is used. Later the plaster has been applied to the surface, finishing of plaster is done to match with the quondam surrounding plaster.

vii. Curing of Plaster
Curing of plaster is necessary to preclude cracking. It should exist done for at least 3 days at regular interval.
8. Finishing of Plaster
Subsequently the plaster is thoroughly cured and stale the surface is then painted with the colour of the surrounding expanse.
Source: https://dreamecons.blogspot.com/2018/10/how-to-repair-plaster-walls.html
Posted by: hodgesrepia1985.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair Old Plaster Walls + "Comment""
Post a Comment